
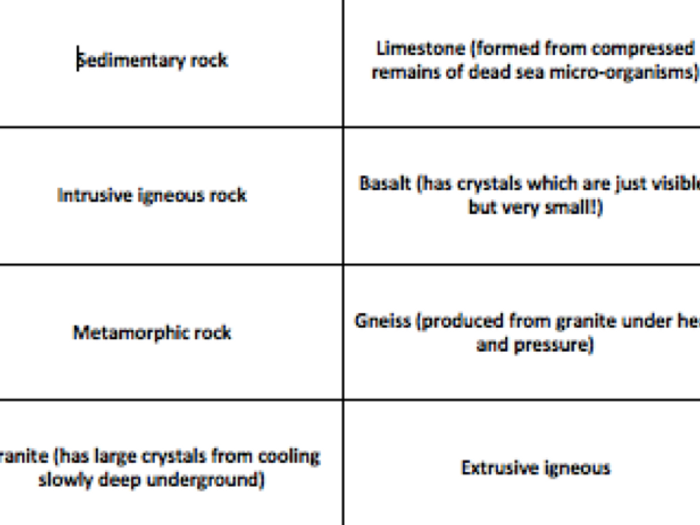
Most of the Earths crust is made of silicon and Silicates are the most common minerals because.Some examples of silicate minerals are olivine,Īugite hornblende, garnet, biotite, albite, and.All silicate minerals contain silicon and oxygen.The largest group of rock forming minerals is the.Sodium (Na) 2.8, Potassium (K) 2.6, Magnesium Relative Abundance Of The Most Common Elements In Minerals can be classified into groups depending.Cleavage The tendency of a mineral to break.Hardness The resistance a mineral offers to.Streak The color of a mineral in its powdered.Light reflected from the surface of a mineral. Luster Luster is the appearance or quality of.Mineral as determined by its internal arrangement Crystal form The external appearance of a.Minerals are the building blocks of rocks.Inorganic crystalline solids that possess a Minerals are defined as naturally occurring,.Still in solid state) by heat, pressure, and/or Pre-existing rock deep within the Earth (but Metamorphic rock is formed by the alteration of.Products of free-existing rocks that have been Sedimentary rock is formed from the weathered.Igneous rock is formed by the crystallization of.Types Of Rocks Continued Igneous Sedimentary, Volcanic cone, landslides (avalanches), dust Examples of faster processes include beachĮrosion during a storm, construction of a.Ranges (tectonism), erosion of mountain ranges. Rock (metamorphism), construction of mountain Re-crystallization of rock to form a different (weathering), chemical cementation of sand grains Rocks, chemical breakdown of rock to form soil Examples of slow processes include formation of.

Processes range from those that occur rapidly to.Rocks in turn are composed of minerals, and.Rocks (including soil, sand, silt, and dust). The materials that make up the Earth are mainly.Weathering processes and turned into new raw When this happens the material is attacked by.Rather, overlying layers may be stripped away,.Metamorphic and sedimentary rocks, as well as.The Rock Cycle Alternative Pathways Continued Transformed directly into metamorphic rocks. When this occurs, the igneous rocks are.Strong compressional forces and high temperatures Eventually these masses may be subjected to the.Weathering and erosion at the Earths surface may Igneous rocks, rather than being exposed to.TheĬhanges, however, take time-great amounts of Although rocks may seem to be unchanging masses,.Sediment from which sedimentary rocks form. Powered by energy from the sun, produce the Weathering and erosion, external processes.Interior are responsible for creating igneous and Processes driven by heat from the Earths.Pressure changes or to still higher temperatures,Įventually crystallize into igneous rock. When metamorphic rock is subjected to additional.The sedimentary rock will react to the changingĮnvironment and turn into metamorphic rock.Magma, it will be subjected to great pressures Mountain building, or intruded by a mass of Within the Earth and involved in the dynamics of If the resulting sedimentary rock is buried deep.Groundwater fills the pores with mineral matter. Rock when compacted by the weight of overlying Sediment is usually lithified into sedimentary.Next, the sediments undergo lithification, a term.Substances are deposited in the ocean, riverįloodplains, desert basins, swamps, and dunes. Eventually these particles and dissolved.Transported by any of a number of erosionalĪgents- running water, glaciers, wind, or waves. The materials, or sediment that result are movedĭown-slope by gravity before being picked up and.Weathering is defined as the disintegration andĭecomposition of igneous rock at or near the.They will undergo a process termed weathering. If the igneous rocks are exposed at the surface,.Surface or, following a volcanic eruption, at the Crystallization may occur either beneath the.Solidifies within the Earth to produce igneous Crystallization- Molten magma cools, and.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
